What and Why of Test Automation in Testing Landscape
Today, Technology and creativity know no bounds. AI, once regarded as science fiction and used as plot material for Hollywood movies, has become a near-ubiquitous technology that is enhancing our daily lives in our workplaces, homes, and across industries.
The market has been inundated with a steady stream of new digital products. The latest innovations have taken the IT world by storm. You can ask complex questions to ChatGPT and receive eerily humanlike responses. You also have a program called Codex that can write computer code; just describe the kind of software issue you’re attempting to fix, and Codex will provide a code solution in the form of a line of code.
The software testing industry too has undergone significant changes in recent years, with test automation becoming increasingly essential for organizations to remain competitive and deliver high-quality software. Test automation has become increasingly important for several reasons, including the speed and complexity of software development, the need for increased efficiency and accuracy, and the limitations of manual testing.
According to GMinsights‘ most recent analysis, Automation Testing is now valued at USD 20 billion and is anticipated to grow at a 15% CAGR between 2023 and 2032.
In this article, we will explore why test automation is so important in today’s software testing industry.
Harnessing Test Automation as a catalyst for change
You cannot talk about the latest practices like DevOps, Continuous Delivery and Continuous Testing without the term Automation.
Applications may have defects in their usability, security, performance, or any combination of those factors. And the inevitable result of this will be a decline in market share, revenue, and customer loyalty. Test automation provides the necessary speed and scale to ensure that software releases are delivered quickly and with high quality, allowing organizations to remain competitive and meet the demands of their customers.
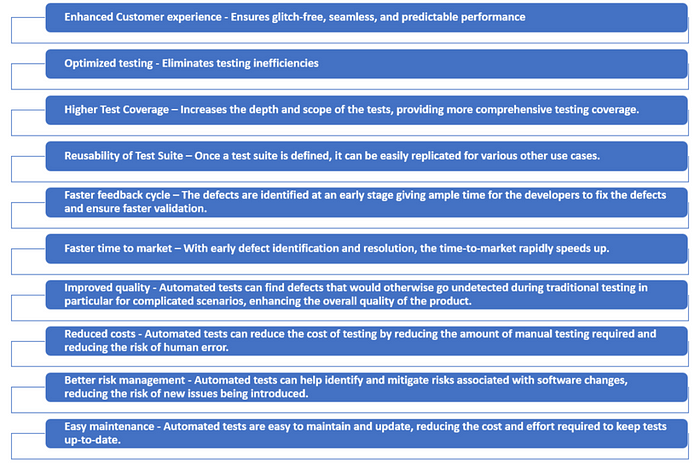
Reducing process lead time and costs through automation of labor-intensive, repetitive tasks frees up human resources for their core competencies and revenue generating tasks. Additional benefits also include:
Top Challenges for making the move to Test Automation
Organizations are realizing the immense potential of intelligent automation — how it increases value and efficiency across business processes. However, few teams are finding it a grueling task to make the move.
The Tricentis Software Fail Watch report states that 314 companies were impacted by software failures, affecting 3.6 billion people and costing $1.7 trillion in lost revenue.
Test Automation has numerous benefits, but it comes with its own set of challenges:

So, how do we Implement a Good Test Automation Strategy?
Despite the fact that automation involves serious effort and dedication, success isn’t that difficult to achieve. The secret is to research, plan, and solve. One of the key needs for the industry is to provide the C-suite and organizations with a roadmap to accelerate, scale, and sustain automation testing adoption.
The Test Automation Strategy defines a framework for automated test scripts. It calls for automating tests at different levels. The foundation and bulk of this test automation pyramid are unit and integration testing. Service layer or API testing is the next step, where the API tests are run against the service layer.
The GUI tests, which are at the top of the pyramid, validate the application as a whole at the presentation layer. Top it up with exploratory testing that identifies potential edge cases. Unlike scripted testing, exploratory testing uncovers unique and out-of-scope defects that would have otherwise been missed.

Although implementing a test automation strategy requires significant time and resource commitment, the rewards can be enormous, including improved quality, lower costs, and greater efficiency.
By following these steps, you can implement a successful test automation strategy that meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your goals:

- Define goals and objectives: Determine what you want to achieve with test automation and what benefits you hope to gain. Answer these 2 questions:
- Which are the features that need testing?
This defines the area of the application which will be automated. - What is the testing approach for each of the selected features?
Defining the scope will help keep all the teams on the same page.
- Assess your current testing environment: Evaluate your current testing processes, tools, and infrastructure to determine what changes need to be made to support test automation.
- Choose the right tools: Choose test automation tools that are appropriate for your specific needs and that align with your goals and objectives.
- Plan and design tests: Plan and design your test automation approach, including how tests will be written, executed, and maintained.
- Build and execute tests: Build and execute your test automation framework, including test cases and test suites.
- Monitor and maintain tests: Monitor the results of your test automation, including test results, performance, and stability, and make any necessary changes to improve the tests.
- Continuously improve: Continuously improve your test automation strategy by reviewing results, addressing any issues, and making changes as needed.
- Integrate with your development process: Integrate your test automation strategy with your development process, including continuous integration and continuous delivery, to ensure that tests are run consistently and that results are available to stakeholders.
Types of Automation Tests
Depending on the project’s needs, the development process, and the testing effort’s objectives, different types of automation tests may be employed.
Let us look at the types of tests that can be automated and how they help test every aspect of the system enabling users to achieve a frictionless experience.
- Unit tests — These tests are used to verify that individual pieces of code, such as functions and methods, behave as intended.
- Integration tests — These tests verify how various components of the system interact with one another to make sure everything functions as it should. Integration tests may involve testing the interactions between different units of code, or between the application and external systems such as databases or APIs.
- Functional tests — functional tests validate the functionality of the system as a whole, from the user’s perspective, involving testing the UI, APIs, and other functional aspects of the application to ensure that they work as expected.
- Regression tests — regression testing is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs after a change.
- Stress tests — Load on the networks results in server outages and network failures. To enhance user experience, stress testing is important to verify the performance on all pages.
- Performance tests — Performance Testing validates the performance and scalability of the system, including response times, resource utilization, and other performance-related metrics. It involves load testing, stress testing, and other types of testing to ensure that the system performs well under different conditions.
- Security tests — Security testing validates the security of the system, including testing for vulnerabilities, data breaches, and other security-related issues. Security tests may involve penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, or other types of testing to ensure that the system is secure. Read for More about :https://www.webomates.com/blog/staying-ahead-of-the-game-why-test-automation-is-a-must-have-in-2023/

