Introduction:
In the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, antibodies have emerged as a crucial element in our battle against the virus. These tiny proteins play a pivotal role in our immune response, providing protection against future infections. However, an important question arises: what is the threshold of protection for COVID-19 antibodies? In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of antibody protection, explore the factors influencing its effectiveness, and shed light on the current scientific understanding. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey to better comprehend the threshold of protection against COVID-19!
Get Well Path Labs
- Understanding Antibodies and Their Role:
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by our immune system to neutralize harmful pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. These proteins recognize specific foreign substances, known as antigens, and help in their elimination from the body. When it comes to COVID-19, antibodies play a crucial role in fighting against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
- Antibody Response to COVID-19:
Upon infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, our immune system mounts a defense by producing antibodies targeting various viral components, including the spike protein. Antibodies can be detected in the bloodstream within days to weeks after infection or vaccination. Two types of antibodies, IgM and IgG, are particularly relevant in the context of COVID-19.
- IgM Antibodies: Early Responders:
The first antibodies to develop in response to an infection are IgM antibodies. They provide an initial line of defense and act as a marker for recent exposure to the virus. However, their levels tend to decline over time, and they are less effective in providing long-term protection.
- IgG Antibodies: Long-Term Protection:
IgG antibodies are the predominant type of antibody produced during later stages of infection or following vaccination. They offer long-term protection by recognizing and neutralizing the virus. The presence of IgG antibodies is indicative of prior infection or successful immunization.
- The Significance of Antibody Levels:
While the presence of antibodies is important, their levels play a crucial role in determining the strength of protection. Higher antibody levels generally correlate with a more robust immune response and better protection against reinfection.
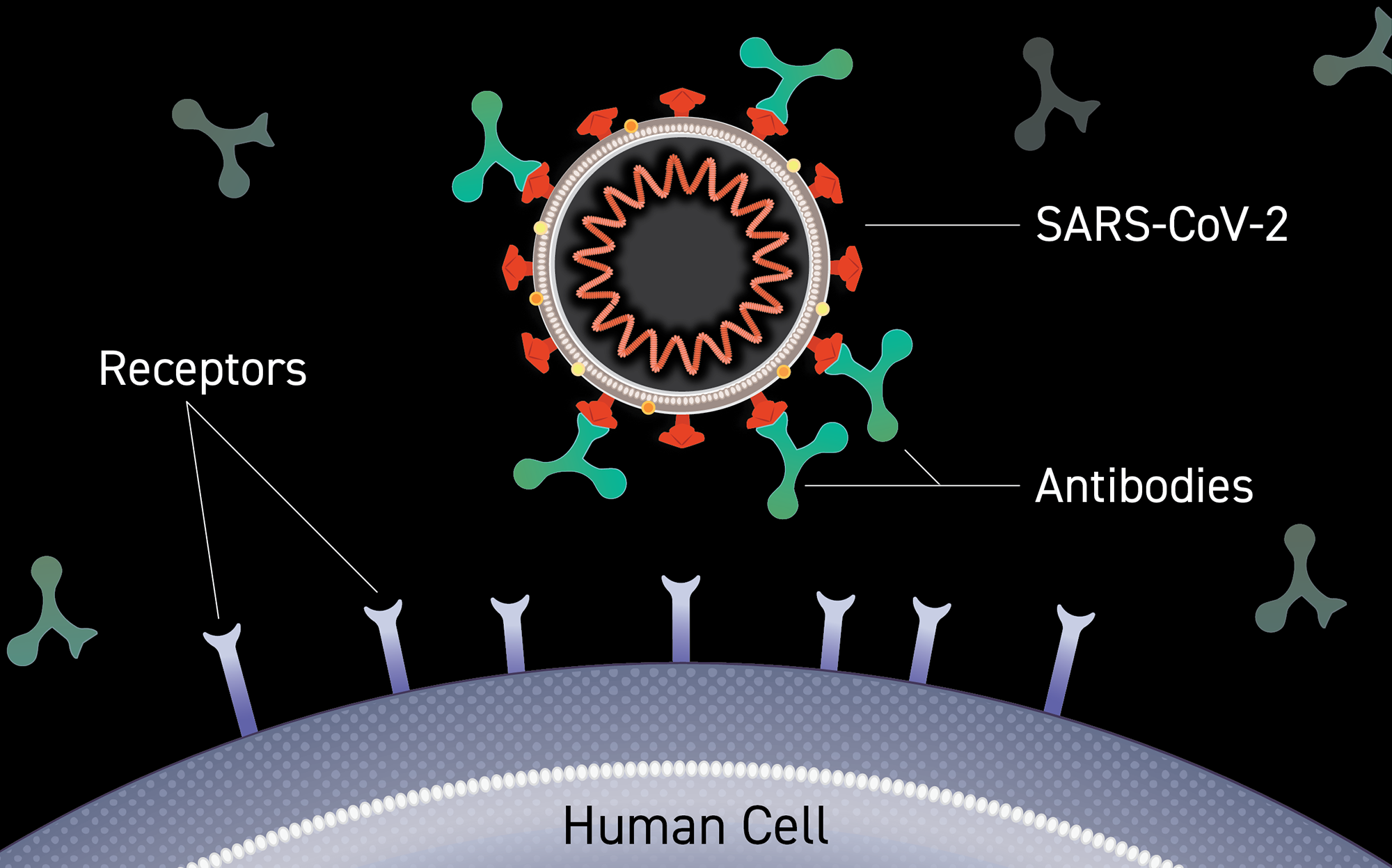
- Variability in Antibody Response:
The antibody response to COVID-19 can vary among individuals. Factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of the infection can influence the magnitude and duration of antibody production. Additionally, emerging variants of the virus may pose challenges in terms of antibody effectiveness.
- Neutralizing Antibodies and Protection:
Not all antibodies are created equal. Neutralizing antibodies are a specific subset that can bind to the virus and prevent it from entering and infecting our cells. These antibodies are of particular interest in assessing the level of protection against COVID-19.
- T-Cell Immunity and Antibodies:
While antibodies are vital in combating the virus, they are not the sole measure of immune protection. T-cell immunity, specifically T-cells known as killer T-cells and helper T-cells, also plays a significant role in eliminating infected cells and orchestrating an effective immune response.
- Duration of Antibody Protection:
Determining the duration of antibody protection against COVID-19 is an ongoing area of research. While antibody levels may decline over time, it is important to note that our immune system possesses memory B-cells that can rapidly produce antibodies upon reexposure to the virus, thus bolstering protection.
- Conclusion:
In conclusion, antibodies are essential in the fight against COVID-19, providing protection against reinfection and potentially reducing the severity of illness. The threshold of protection for COVID-19 antibodies.

