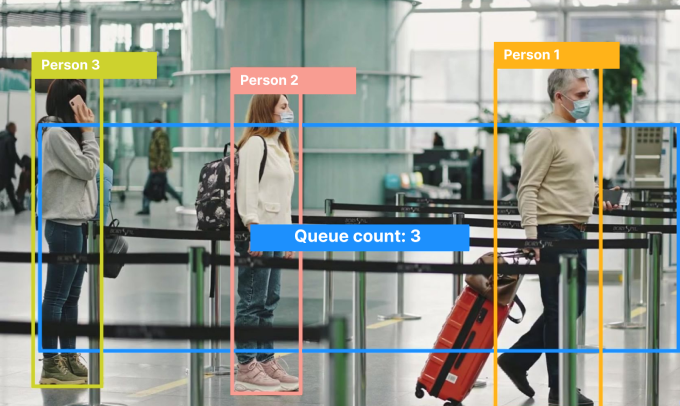
In today’s fast-paced world, queue management is more critical than ever. Whether it’s in retail stores, banks, airports, or healthcare facilities, long queues are a frequent source of frustration for customers and inefficiencies for businesses. As the world becomes more technologically advanced, traditional queue management methods are evolving. One of the most innovative and effective approaches to modern queue management is the use of computer vision (CV) technology.
In this article, we will explore how cutting-edge computer vision solutions are revolutionizing queue management systems, making them smarter, more efficient, and customer-friendly.
Understanding Queue Management Challenges
Computer vision, a branch of artificial intelligence (AI), enables machines to interpret and understand visual data from the world around them. By applying Computer Vision in Queue Management, businesses can address the challenges mentioned above, ensuring better service delivery and improved operational efficiency.
Here’s how computer vision transforms the way queues are managed:
1. Real-Time Queue Monitoring
Computer vision technology can continuously monitor queues in real time through the use of surveillance cameras and image processing algorithms. With machine learning models, CV systems can track the movement of individuals in line and assess the length and flow of queues.
By collecting real-time data, businesses can:
- Identify when a queue is getting too long or slow-moving.
- Alert staff or automatic systems to intervene before customer frustration peaks.
- Predict peak times and optimize staff or resources accordingly.
This kind of real-time intelligence is a game-changer, as it allows businesses to respond immediately to changing conditions.
2. Customer Behavior Analysis
Queue management systems powered by computer vision not only track the physical length of the queue but also offer insights into customer behavior. For example:
- Dwell Time: CV systems can calculate how long a customer stands in line, providing valuable data on service efficiency.
- Customer Patience: Computer vision algorithms can analyze customer behavior, such as restlessness or impatience, by assessing their movements and facial expressions. This enables staff to address issues before they escalate.
By collecting and analyzing such behavioral data, businesses can tailor their services to ensure a more comfortable and less stressful customer experience.
3. Automated Queue Navigation
In environments such as airports, shopping malls, or retail stores, computer vision can help manage queues automatically by guiding customers to available lines. This is particularly useful in self-service settings, where customers might struggle to decide which line to join.
- Dynamic Queue Allocation: Based on real-time data, computer vision systems can suggest the most efficient queue for a customer, guiding them via signage or digital displays.
- Optimized Movement: Using facial recognition or other tracking techniques, CV systems can direct customers to shorter or faster-moving lines, optimizing the flow of people.
Automated queue navigation improves the customer experience by reducing confusion and wait times.
4. Virtual Queueing Systems
With the help of computer vision, virtual queueing solutions are becoming increasingly popular. Instead of physically standing in a line, customers can check-in using a mobile app, and their place in the queue is monitored digitally.
- Facial Recognition: CV systems can identify customers through facial recognition, confirming their place in the virtual queue without the need for physical tokens or barcodes.
- Real-Time Updates: Customers can receive real-time updates on their position in the queue, allowing them to spend their waiting time productively elsewhere.
This technology is particularly useful in sectors such as healthcare, where patients can wait in a comfortable space until it’s their turn, or retail, where customers can roam the store without the hassle of waiting in line.
5. Crowd Management and Social Distancing
In today’s environment, especially in high-density locations like airports, events, and hospitals, managing crowds while ensuring safety is paramount. Computer vision plays a crucial role in this area.
- Social Distancing Monitoring: CV systems can track the distance between individuals in a queue and trigger alerts if people are not maintaining proper social distance.
- Crowd Density Monitoring: CV technology can assess the number of people in a given area, helping businesses control crowd density and avoid over-congestion.
- Traffic Flow Control: In venues where multiple queues converge, computer vision systems can assess and redirect the flow of people to prevent crowd bottlenecks.
By using AI-powered vision systems, businesses can ensure not only the safety of their customers but also a seamless and efficient experience.
6. Data Analytics and Reporting
One of the most significant benefits of implementing computer vision in queue management is the ability to collect vast amounts of data for analysis and reporting. Businesses can track:
- Peak Hours: Identifying the busiest times of the day or week allows businesses to better allocate staff and resources.
- Queue Duration: Tracking how long customers spend in line helps in optimizing staff schedules and operational workflows.
- Customer Demographics: By analyzing customers’ facial expressions and movements, CV systems can collect insights about customer moods and preferences.
This data empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions that enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Practical Applications of Computer Vision in Queue Management
- Retail: In retail, computer vision can be used for monitoring checkout queues, guiding customers to shorter lines, and optimizing store layouts. In some advanced setups, it can even track how long customers stay at the checkout counter and suggest ways to streamline the process.
- Airports: Airports can use CV to monitor check-in and security lines, helping staff direct passengers to open counters. It can also be used for crowd control and maintaining security.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics use computer vision to track patient waiting times and monitor queues at registration desks, pharmacies, or treatment areas. This allows them to allocate staff and resources effectively.
- Banks: Banks can use computer vision for monitoring waiting times in queues at tellers and self-service kiosks. AI systems can prioritize urgent customer needs and automatically alert staff when additional help is required.
- Events & Entertainment: For events, CV can manage entry lines, optimize food & beverage queues, and track the density of people at various locations within the venue, ensuring a smooth, enjoyable experience.
Challenges and Considerations
While computer vision offers numerous advantages, its implementation also comes with challenges:
- Privacy Concerns: Facial recognition and behavioral monitoring raise significant privacy issues. It’s essential to ensure that customer data is handled securely and in compliance with privacy regulations.
- High Initial Investment: Implementing a comprehensive computer vision-based queue management system requires investment in hardware, software, and training.
- System Complexity: Integrating computer vision with existing queue management infrastructure can be complex and requires skilled personnel.
Conclusion
Computer vision technology has emerged as a revolutionary tool for modern queue management. By leveraging real-time monitoring, customer behavior analysis, automated navigation, and virtual queueing, businesses can enhance the customer experience, optimize resource allocation, and improve operational efficiency. As this technology continues to advance, it will undoubtedly play a critical role in the future of queue management across industries.
While the challenges are real, the potential benefits of integrating cutting-edge computer vision into queue management systems are immense. With tools like AI Video analytics software, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of customer patterns and make data-driven decisions that improve both service and efficiency. Early adopters of this technology can gain a competitive edge in offering superior customer service and operational efficiency.