Solenoid valves are essential components widely used in various industrial applications. They provide efficient safety Considerations in Working with Pneumatic Directional Control Valves.
Importance of Safety in Working with Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Ensuring safety is of utmost importance when working with pneumatic directional control valves. These valves are critical in controlling compressed air flow in various industrial applications. Failure to follow proper safety procedures can result in accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of safety when working with pneumatic directional control valves:
- Protection against Hazards: Pneumatic systems involve high-pressure air, and mishandling of directional control valves can lead to hazards such as sudden releases of pressure, uncontrolled movements, or unexpected valve operations. Adhering to safety protocols minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
- Training and Education: Proper training and education are essential for personnel working with pneumatic directional control valves. Understanding the principles of pneumatic systems, valve functions, and safety procedures ensures competent and knowledgeable equipment handling. This knowledge empowers operators to identify potential risks and take appropriate precautions.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wearing the appropriate personal protective equipment is crucial when working with pneumatic directional control valves. Safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection are examples of PPE that can safeguard workers from potential hazards associated with compressed air and valve operations.
- Safe Installation and Maintenance: Following safe installation and maintenance practices is essential for the longevity and efficient operation of pneumatic directional control valves. Regular inspections, lubrication, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can help prevent valve malfunctions and minimize the risk of accidents.
- Consideration of Long Stroke Air Cylinder: When working with pneumatic directional control valves, it is important to consider the system’s specific requirements. For applications involving long-stroke air cylinders, proper safety measures should be implemented to ensure the stability and controlled movement of the cylinder throughout its stroke range.
Organizations can create a secure and productive work environment by prioritizing safety with pneumatic directional control valves. Strict adherence to safety protocols, continuous training, and a proactive approach to risk management will safeguard employees and optimize the performance and longevity of the pneumatic system.
Understanding the Hazards Associated with Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Pneumatic directional control valves are vital components in pneumatic systems, allowing for the regulation and control of airflow. While these valves offer numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential hazards associated with their operation. By understanding these hazards, users can take appropriate precautions to ensure their safety and the safety of those around them.
- High-Pressure Hazards: Pneumatic directional control valves are often used in systems that operate at high-pressure levels. The release of compressed air at high pressures can result in severe injuries. Users must be cautious when working with these valves and ensure proper pressure regulation and relief mechanisms are in place.
- Airborne Particles and Contaminants: Pneumatic systems can generate airborne particles and contaminants during operation. These can include dust, debris, or oil mist. Inhaling these particles can pose health risks, such as respiratory problems. Proper filtration and maintenance of pneumatic systems are essential to minimize the presence of airborne contaminants.
- Noise Exposure: Pneumatic systems, including directional control valves, can produce high noise levels during operation. Prolonged exposure to excessive noise levels can lead to hearing loss or other hearing-related issues. Hearing protection should be worn when working near pneumatic systems to mitigate the risks associated with noise exposure.
- Mechanical Hazards: Pneumatic directional control valves have moving parts that can pose mechanical hazards if incorrectly handled. Pinching, crushing, or entanglement injuries can occur if fingers, hands, or clothing gets caught in the valve mechanisms. Following proper lockout/tagout procedures, using guarding devices, and avoiding reaching into moving parts are essential safety practices.
- Electrical Hazards: In some pneumatic systems, electrical components may be integrated with directional control valves. This introduces the risk of electrical hazards, such as electric shock or short circuits. Users should adhere to electrical safety guidelines and ensure proper grounding and insulation of electrical components.
Users can implement appropriate safety measures to protect themselves and others by understanding the hazards associated with pneumatic directional control valves. Regular maintenance, proper training, and adherence to safety protocols are crucial for safe operation and preventing accidents or injuries related to pneumatic systems and their components, including the pneumatic directional control valve.
Proper Training and Education for Safe Handling of Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Pneumatic directional control valves are crucial in controlling compressed air flow in pneumatic systems. However, due to the potential hazards associated with high-pressure air and the complexity of these valves, it is essential to receive proper training and education to ensure their safe handling. Below are some key points highlighting the importance of training and education in this regard:
- Knowledge of Valve Operation: Training should cover pneumatic directional control valves’ fundamental principles and working mechanisms. Understanding how these valves function, including their various components and operating principles, is crucial for safe operation.
- Safety Precautions: Training programs should emphasize the importance of safety precautions when working with pneumatic directional control valves. This includes understanding the risks associated with compressed air, such as high-pressure releases, and using personal protective equipment (PPE) to mitigate those risks.
- Installation and Maintenance Procedures: Proper training should cover the correct installation and maintenance procedures for pneumatic directional control valves. This includes guidelines for proper valve mounting, connection, adjustment, and routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection.
- Troubleshooting and Problem-Solving: Training programs should equip individuals with the necessary skills to identify and troubleshoot common issues that may arise with pneumatic directional control valves. This includes recognizing and addressing leaks, blockages, and abnormal valve behavior.
- Compliance with Standards and Regulations: Educating individuals on relevant industry standards and regulations governing safely handling pneumatic directional control valves is essential. This ensures adherence to safety guidelines and helps prevent accidents or injuries.
By providing proper training and education on safely handling pneumatic directional control valves, individuals can gain the necessary knowledge and skills to operate these valves safely and efficiently. This reduces the risk of accidents and injuries and promotes the longevity and optimal performance of the pneumatic system. Therefore, investing in comprehensive training programs and ongoing education is crucial for anyone working with pneumatic directional control valves.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Requirements for Working with Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
When working with pneumatic directional control valves, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent potential accidents or injuries. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) ensures the well-being of individuals involved in these valves’ operation, installation, or maintenance. Here are some essential PPE requirements to consider:
- Eye Protection: Pneumatic systems can involve high-pressure air and the potential for airborne particles or debris. Safety glasses or goggles with side shields are necessary to protect the eyes from possible hazards.
- Hand Protection: Hands are particularly vulnerable during valve installation or maintenance tasks. Appropriate gloves, such as cut-resistant or grip-enhancing, can shield hands from cuts, abrasions, or pinch points.
- Foot Protection: Heavy equipment or materials may pose a risk of foot injuries. Sturdy, steel-toed boots or safety shoes can provide adequate protection against potential crushing or impact hazards.
- Respiratory Protection: In environments with a risk of inhaling harmful airborne contaminants, such as dust, fumes, or gasses, respiratory protection may be necessary. Respirators, such as N95 masks or air-purifying respirators, should be used as per the specific hazards present.
- Hearing Protection: Pneumatic systems can generate high noise levels, especially during valve operation. Earplugs or earmuffs should be worn to prevent hearing damage or loss.
- Protective Clothing: Additional protective clothing may be required depending on the work environment. This could include coveralls, aprons, or flame-resistant garments to safeguard against chemical splashes, burns, or electrical hazards.
Remember, PPE requirements may vary based on the risks associated with your workplace’s pneumatic directional control valve operations. Conduct a thorough risk assessment and ensure that all personnel are properly trained in correctly using, maintaining, and storing PPE.
By adhering to the appropriate PPE requirements, individuals can minimize the potential risks and hazards while working with pneumatic directional control valves, ensuring a safer and more secure work environment.
Safe Installation and Maintenance Practices for Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Installing and maintaining pneumatic directional control valves require careful attention to safety protocols to ensure these critical components’ smooth and reliable operation. By following proper practices, you can mitigate potential hazards and extend the lifespan of the valves. Here are some important guidelines to consider:
Planning and Preparation:
- Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s instructions and specifications for the specific pneumatic directional control valve model you are working with.
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards and take necessary precautions.
- Ensure you have the appropriate tools and equipment for the installation and maintenance procedures.
Handling and Storage:
- Handle the pneumatic directional control valves carefully to prevent damage to sensitive components.
- Avoid dropping or applying excessive force during transportation or storage.
- Store the valves in a clean, dry area away from corrosive substances and extreme temperatures.
Proper Mounting and Connection:
- Ensure the valve is securely mounted to prevent vibrations and movement during operation.
- Follow the recommended torque specifications for fasteners to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Use appropriate sealing materials to achieve leak-free connections.
Electrical Safety:
- When working with pneumatic directional control valves with electrical components, ensure the power is switched off before making any connections or adjustments.
- Use insulated tools and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect against electrical hazards.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance:
Implement a routine inspection schedule to identify any signs of wear, leaks, or damage.
Clean the valves periodically to remove debris and contaminants that could impair performance.
Replace worn-out parts or damaged components promptly to prevent potential failures.
Remember, the safe installation and maintenance of pneumatic directional control valves are crucial for the overall safety and efficiency of pneumatic systems. By following these practices, you can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your pneumatic directional control valves, promoting a secure working environment for everyone involved.
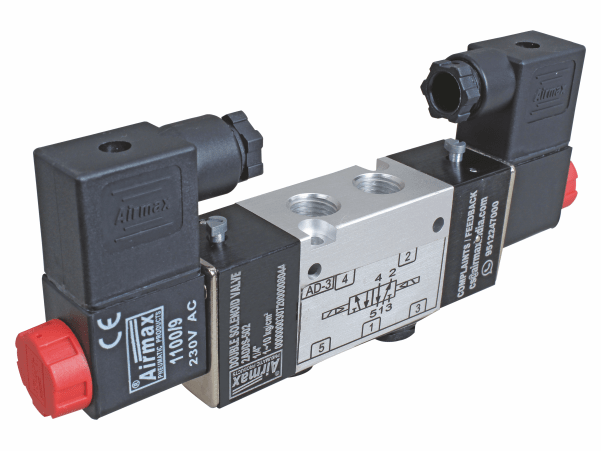
Precautions for Handling Compressed Air in Pneumatic Systems
Compressed air is a critical component in pneumatic systems, providing the power necessary to operate various devices such as pneumatic directional control valves. However, it is essential to observe certain precautions when working with compressed air to ensure safe and efficient system performance. Here are some key precautions to consider:
- Adequate Pressure Regulation: Proper pressure regulation is crucial to prevent overpressurization of the system, which can lead to component failure or even rupture. Ensure the pressure is regulated within the recommended range for the pneumatic directional control valve and other system components.
- Pressure Relief: Install pressure relief valves or devices to safeguard against excessive pressure buildup. These devices will automatically relieve excess pressure, protecting the system and its components from potential damage.
- Regular Inspection: Conduct routine inspections of the compressed air system, including pneumatic hoses, fittings, and connections. Look for signs of wear, damage, or leaks, and promptly replace or repair any compromised components.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all pneumatic connections are properly secured and tightened. Loose connections can result in air leaks, leading to system inefficiencies and potential hazards.
- Proper Filtration: Incorporate appropriate filtration systems to remove contaminants from the compressed air supply. Dust, dirt, moisture, and other impurities can negatively impact the performance and lifespan of pneumatic directional control valves and other system components.
- Use Compatible Lubricants: If lubrication is necessary for the pneumatic directional control valve or other devices, ensure that only compatible lubricants are used. Incompatible lubricants can cause damage and affect the overall operation of the system.
- Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential, especially in enclosed spaces with compressed air systems. Proper ventilation helps dissipate heat generated by the system and prevents the accumulation of potentially harmful fumes.
Remember, these precautions are general guidelines, and it is essential to consult the manufacturer’s instructions and recommendations for the pneumatic directional control valve and the pneumatic system being used. By following these precautions, you can ensure the safe and reliable operation of pneumatic directional control valves and maintain the overall integrity of the pneumatic system.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures for Maintenance and Repair of Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Maintenance and repair activities involving pneumatic directional control valves require strict adherence to safety procedures to prevent accidents and injuries. One crucial safety measure is implementing lockout/tagout procedures, which involve isolating and securing the equipment to protect workers from hazardous energy sources. Here are some key points to consider when implementing lockout/tagout procedures for pneumatic directional control valves:
- Importance of Lockout/Tagout: Lockout/Tagout procedures are essential for ensuring the safety of maintenance and repair personnel by preventing accidental energization of pneumatic directional control valves. These valves control compressed air flow and can pose serious risks if not properly de-energized before maintenance work.
- Identify Energy Sources: Before initiating any maintenance or repair task, it is crucial to identify and locate all energy sources associated with the pneumatic directional control valve system. This may include electrical power, compressed air supply, and any potential stored energy within the system.
- Equipment Shutdown: Properly shut down the pneumatic system by turning off the power supply and releasing any stored energy. Depressurize the system by opening valves downstream from the control valve and bleeding off residual air pressure.
- Lockout/Tagout Devices: Apply lockout devices such as padlocks or lockout hasps to secure the energy isolation points. Use tags to communicate the reason for the lockout and the identity of the authorized personnel performing the maintenance or repair.
- Verification and Testing: After implementing lockout/tagout procedures, verify that the pneumatic directional control valve and associated equipment are de-energized. Test the system by attempting to operate the valve or using appropriate testing devices to ensure zero energy flow.
- Safe Work Practices: While performing maintenance or repair tasks, follow safe work practices such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), using insulated tools, and working with a partner or in the presence of a designated observer.
By diligently following lockout/tagout procedures, workers can effectively mitigate the risks of maintaining and repairing pneumatic directional control valves. These procedures enhance safety, prevent accidents, and protect the well-being of personnel working on pneumatic systems.
Identifying and Addressing Potential Leaks in Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
Pneumatic directional control valves are critical in regulating compressed air flow in various industrial applications. However, like any mechanical system, they can develop leaks over time, leading to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and even safety hazards. Identifying and addressing potential leaks in pneumatic directional control valves is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prevent costly downtime. Here are some key points to consider:
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection of the pneumatic directional control valve and its associated components. Look for any signs of leakage, such as visible air or fluid escaping from connections, fittings, or seals.
- Pressure Drop Testing: Perform a pressure drop test by measuring the pressure upstream and downstream of the valve. A significant pressure drop indicates the presence of a leak.
- Ultrasonic Leak Detection: Utilize ultrasonic leak detection devices to identify high-frequency sounds produced by air leaks. These devices can pinpoint the exact location of the leak, allowing for targeted repairs.
- Seal and Gasket Inspection: Check the seals and gaskets of the pneumatic directional control valve for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration. Replace any faulty seals or gaskets promptly.
- Tightening and Securing Connections: Ensure all connections, fittings, and fasteners are properly tightened. Loose connections can lead to air leakage.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a preventive maintenance program for pneumatic directional control valves. Regularly inspect and clean the valves, lubricate moving parts, and replace worn-out components.
- Training and Education: Train personnel with pneumatic directional control valves on leak detection techniques, proper installation procedures, and maintenance protocols.
By proactively identifying and addressing potential leaks in pneumatic directional control valves, you can optimize their performance, reduce energy waste, and enhance the overall efficiency of pneumatic systems. Regular inspections, pressure testing, and maintenance are essential to ensure the reliability and safety of these critical components.
Remember, promptly addressing leaks improves the longevity of the pneumatic directional control valve and minimizes the risk of system failures and costly repairs. Therefore, prioritizing leak detection and prevention should be integral to any maintenance strategy involving pneumatic directional control valves.
Safe Pressure Regulation and Relief in Pneumatic Systems
Proper pressure regulation and relief are crucial for ensuring pneumatic systems’ safe and efficient operation, including those incorporating pneumatic directional control valves. Failure to maintain appropriate pressure levels can lead to system malfunctions, component damage, and potential safety hazards. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to safe pressure regulation and relief in pneumatic systems:
- Set operating pressure: Determine the proper operating pressure for your specific pneumatic system, considering factors such as the capacity of the components and the desired performance. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for the pneumatic directional control valve to ensure accurate pressure settings.
- Pressure regulators: Install high-quality pressure regulators to maintain a consistent and controlled pressure level within the system. These devices allow you to adjust and stabilize the pressure according to the application’s requirements. Regularly inspect and calibrate pressure regulators to ensure accurate and reliable operation.
- Pressure relief valves: Incorporate pressure relief valves into your pneumatic system as a safety measure. These valves release excess pressure when it exceeds a predetermined level, protecting the system from overpressurization and potential damage. Ensure the pressure relief valve is properly sized and set to the appropriate relief pressure.
- Monitoring and maintenance: Implement a routine monitoring and maintenance schedule to ensure the pressure regulation and relief mechanisms are functioning correctly. Regularly inspect pressure gauges, regulators, and relief valves for any signs of damage or malfunction. Address any issues promptly to prevent potential hazards.
- Training and education: Provide proper training and education to operators and maintenance personnel about the safe operation and maintenance of pneumatic systems, emphasizing the importance of pressure regulation and relief. Ensure they understand the risks associated with improper pressure levels and how to respond to pressure-related emergencies.
By implementing these practices, you can ensure safe pressure regulation and relief in your pneumatic system, including the directional control valve. This helps prevent system failures, damage to components, and potential safety hazards, ultimately optimizing the performance and longevity of the system.
Emergency Shutdown Procedures for Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
In industrial settings, where pneumatic directional control valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of compressed air, it is essential to have well-defined emergency shutdown procedures. These procedures ensure the safety of personnel and equipment in case of emergencies or critical situations. Here are some key considerations and steps to follow during an emergency shutdown involving pneumatic directional control valves:
- Immediate Recognition: Quickly identify any signs of an emergency, such as abnormal pressure levels, leaks, or malfunctioning equipment.
- Communication: Inform all relevant personnel about the emergency and the need for an immediate shutdown. Use clear and concise language to avoid confusion.
- Emergency Stop Button: Locate and press the emergency stop button or switch, if available, to halt the operation of the pneumatic directional control valve and associated equipment. This action will interrupt the compressed air supply and keep the system safe.
- Isolate Power: Cut off the power supply to the pneumatic directional control valve and any connected machinery. This step prevents accidental restarts and ensures the safety of personnel during maintenance or troubleshooting.
- Ventilation: Open any ventilation systems to dissipate potentially hazardous gases or fumes that may have accumulated due to the emergency.
- Assess the Situation: Evaluate the cause and severity of the emergency, considering factors such as pressure levels, temperature, leaks, and the overall condition of the pneumatic system.
- Report and Notify: Inform relevant personnel, such as supervisors, maintenance technicians, or safety officers, about the emergency and its details. Report any damages or incidents that occurred as a result of the emergency shutdown.
- Repair and Inspection: Once the emergency has been addressed and the system is safe, initiate the necessary repairs or maintenance procedures on the pneumatic directional control valve. Conduct a thorough inspection to identify the root cause and prevent similar emergencies in the future.
Remember, the emergency shutdown procedures may vary depending on the specific system and industry. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and complying with applicable safety regulations is crucial to proper handling and operating pneumatic directional control valves.
Pneumatic directional control valves are essential components in industrial systems, and having well-established emergency shutdown procedures is vital to safeguarding personnel and equipment in critical situations. Fluid flow control is crucial in automating processes, enhancing safety, and improving productivity. Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that use an electrical current to control the opening and closing of a valve, allowing or blocking the flow of liquids or gasses.
Key points to consider about the industrial applications of solenoid valves:
- Versatility: Solenoid valves are highly versatile and find applications in a wide range of industries, such as oil and gas, automotive manufacturing, food processing, water treatment, HVAC, pharmaceutical manufacturing, agriculture, packaging, and chemical processing.
- Fluid Control: Solenoid valves control the flow, pressure, and direction of various fluids, including liquids, gases, steam, and even corrosive or hazardous substances.
- Automation: Solenoid valves are vital components in automated systems where precise and rapid fluid control is required. They enable efficient automation of processes, reducing manual intervention and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Safety: Solenoid valves are crucial in maintaining safety in industrial applications. They can quickly shut off the flow of fluids in emergencies, preventing accidents, leaks, and system failures.
- Reliability: Solenoid valves are known for their reliability and durability, ensuring consistent performance even in harsh environments or demanding operating conditions.
- Integration: Solenoid valves can be easily integrated into existing systems or new designs. They are compatible with various control systems, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or distributed control systems (DCS).
- Pneumatic Control Valve: One specific application of solenoid valves is in pneumatic control systems. Pneumatic control valves utilize compressed air to control the flow of fluids, making them an efficient and widely used solution in industrial settings.
In conclusion, solenoid valves are essential components with various industrial applications. Their versatility, reliability, and ability to provide precise fluid control make them indispensable in various industries. Whether it’s controlling the flow of oil in a refinery, regulating the temperature in an HVAC system, or automating processes in a manufacturing plant, solenoid valves are key to improving efficiency, safety, and productivity.
Solenoid Valves in Oil and Gas Industry: Applications and Benefits
The oil and gas industry heavily relies on various types of valves for the efficient and safe operation of its processes. Among these valves, solenoid valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of fluids and gasses in different applications. Let’s explore the applications and benefits of solenoid valves in the oil and gas industry.
Applications of Solenoid Valves:
- Wellhead Control: Solenoid valves are used in wellhead control systems to regulate the flow of oil or gas from the well. They help shut off or divert the flow during emergencies, ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
Pipeline Control: Solenoid valves are employed in pipeline systems to control the flow of oil or gas, enabling efficient transportation from extraction sites to refineries or distribution points. They are used for opening and closing pipelines, as well as for regulating pressure and flow rates.- Safety Systems: Solenoid valves are integral to safety systems in oil and gas facilities. They are utilized in emergency shutdown systems (ESDs) to quickly isolate sections of pipelines or equipment during hazardous situations, such as leaks or fires.
Benefits of Solenoid Valves:
- Fast Response Time: Solenoid valves offer rapid response times, allowing quick and precise control over fluid or gas flow. This is crucial in critical situations where immediate action is necessary to prevent accidents or minimize damage.
- Reliability: Solenoid valves are known for their reliability and durability. They can withstand harsh operating conditions, including high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for the demanding environments of the oil and gas industry.
- Remote Operation: Solenoid valves can be operated manually or through automation systems. This feature enables efficient and convenient control of flow without the need for physical intervention, increasing operational efficiency.
- Compact Design: Solenoid valves are compact, making them space-efficient for installation in oil and gas equipment and systems. Their small size allows for flexibility in design and ease of integration into existing infrastructure.
In conclusion, solenoid valves are indispensable in the oil and gas industry due to their diverse applications and numerous benefits. From wellhead control to pipeline operations and safety systems, solenoid valves provide efficient and reliable flow control, ensuring the smooth and safe operation of oil and gas processes.
Solenoid Valves in Automotive Manufacturing: Enhancing Efficiency and Control
Solenoid valves are vital in enhancing efficiency and control throughout various processes in the automotive manufacturing industry. These valves are electromechanical devices that use an electrical current to control the flow of fluids or gasses. In automotive manufacturing, solenoid valves offer several advantages that contribute to improved efficiency and precise control. Let’s explore some key points highlighting the significance of solenoid valves in this industry:
- Fluid Control in Engine Systems: Solenoid valves are commonly used in engine systems to regulate the flow of coolant, oil, and fuel. They ensure the optimal distribution of fluids to different engine components, contributing to improved performance and fuel efficiency.
- Transmission and Gear Shift Control: Solenoid valves are employed in automatic transmissions to control the shifting of gears. They enable smooth gear transitions and precise timing, enhancing the driving experience and reducing wear on transmission components.
- Emission Control Systems: Solenoid valves are integral to vehicle emission control systems. They regulate the flow of gases, such as exhaust or evaporative emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and minimizing harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere.
- Brake Systems: Solenoid valves are crucial in anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and traction control systems (TCS). By controlling the flow of hydraulic pressure, solenoid valves enable quick and precise modulation of brake force, enhancing safety and vehicle control during braking and cornering.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS): Solenoid valves are utilized in TPMS to monitor and adjust tire pressure. They allow for automatic inflation or deflation of tires based on predefined thresholds, optimizing fuel efficiency, tire lifespan, and overall vehicle performance.
Overall, solenoid valves are indispensable components in automotive manufacturing. They enhance efficiency and control by precisely regulating fluid flow, ensuring optimal performance of engine systems, transmissions, emission control systems, braking systems, and tire pressure monitoring. With their reliable and responsive operation, solenoid valves contribute to safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly vehicles.
Solenoid Valves in Food Processing Industry: Ensuring Safety and Quality
The food processing industry is one of the most critical sectors where safety and quality are paramount. Solenoid valves are crucial in maintaining these standards by ensuring precise fluid control and hygienic operations. Let’s explore how solenoid valves contribute to the safety and quality of food processing:
- Hygienic Fluid Control: Solenoid valves are designed to meet strict hygiene requirements in the food industry. They are constructed with corrosion-resistant materials and withstand harsh cleaning agents and high temperatures. This ensures that the valves do not contaminate the food products during processing.
- Flow Control and Accuracy: Solenoid valves provide precise control over the flow of liquids or gases in food processing applications. They can accurately regulate the flow rate, pressure, and temperature, allowing manufacturers to maintain consistency in their processes and produce high-quality products.
- Automation and Efficiency: Solenoid valves can be easily integrated into automated food processing systems. Their electrically operated design enables quick and reliable response times, allowing efficient fluid flow control. This automation reduces manual handling and minimizes the risk of human error, thereby improving overall safety and productivity.
- Contamination Prevention: Solenoid valves feature a closed-off design when not in operation, preventing the entry of contaminants such as dust, dirt, and microorganisms into the processing lines. This helps maintain the food products’ integrity and prevents potential health hazards.
- Safety Shut-off: In case of emergencies or system malfunctions, solenoid valves can serve as safety shut-off devices. They can quickly close off the flow of fluids, isolating specific sections of the processing line to prevent contamination or damage.
Integrating solenoid valves in food processing equipment ensures that safety and quality standards are met throughout production. Their hygienic design, precise control, automation capabilities, and safety features make them indispensable components in maintaining the integrity of food products. Solenoid valves play a vital role in guaranteeing the safety of consumers and upholding the reputation of food processing companies in delivering high-quality products.
Solenoid Valves in Water Treatment Systems: Improving Flow Control and Monitoring
Water treatment systems are critical in ensuring clean and safe water for various residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Within these systems, solenoid valves are integral components that contribute to efficient flow control and monitoring. Let’s explore how solenoid valves enhance water treatment processes:
- Flow Control: Solenoid valves regulate water flow in different water treatment systems stages. These valves offer precise control over the amount of water passing through pipelines, allowing for optimal distribution and allocation of water resources. Operators can adjust the flow rates according to specific requirements using solenoid valves, ensuring a consistent and reliable water supply.
- Remote Operation: Solenoid valves often have electrical actuators that enable remote operation and control. This feature is particularly beneficial in water treatment systems where the valves may be located in hard-to-reach or hazardous areas. With solenoid valves, operators can conveniently open, close, or adjust the valves remotely, improving operational efficiency and reducing manual labor.
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Solenoid valves in water treatment systems are often designed with fail-safe mechanisms to ensure operational reliability and prevent water wastage. In case of power failure or other system disruptions, these valves automatically default to a closed position, preventing any uncontrolled flow or leakage. This feature helps to maintain the integrity of the water treatment process and minimize the risk of water contamination.
- Monitoring Capabilities: Advanced solenoid valves incorporate monitoring capabilities such as position sensors or feedback mechanisms. These sensors provide real-time information about the status and position of the valve, allowing operators to monitor its performance. Integrating solenoid valves with monitoring systems can promptly detect potential issues, such as valve malfunctions or blockages, enabling timely maintenance and preventing costly downtime.
In conclusion, solenoid valves play a vital role in water treatment systems by improving flow control and monitoring. These valves enable precise water flow regulation, offer remote operation capabilities, incorporate fail-safe mechanisms, and provide monitoring features for enhanced system efficiency. With their reliable performance and versatile applications, solenoid valves contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of water treatment processes.
Solenoid Valves in HVAC Systems: Optimizing Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are crucial in maintaining comfortable indoor environments. Among the various components of an HVAC system, solenoid valves are essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of these systems. Solenoid valves, controlled by electric currents, regulate the flow of fluids such as water or refrigerant in HVAC applications. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of solenoid valves in HVAC systems:
- Precise Temperature Control: Solenoid valves enable precise temperature control in HVAC systems by regulating the flow of hot or cold fluids. By adjusting the opening and closing of the valve, the desired temperature can be maintained effectively.
- Energy Efficiency: HVAC systems are major consumers of energy in buildings. Solenoid valves contribute to energy efficiency by allowing selective heating or cooling in different zones or areas. This zoning capability helps reduce energy wastage by delivering conditioned air only where it is needed.
- Fault Detection and Safety: Solenoid valves equipped with sensors can detect abnormalities such as pressure drops or leaks in the HVAC system. They can automatically shut off the flow of fluids to prevent damage, ensuring the system’s and occupants’ safety.
- System Protection: Solenoid valves act as protective devices by preventing the flow of fluids during system startup or shutdown. This safeguards the HVAC system and its components from potential damage caused by sudden pressure surges or inadequate lubrication.
- Remote Control and Automation: Solenoid valves can be integrated into HVAC control systems, allowing remote operation and automation. This enables efficient scheduling, optimization, and monitoring of heating and cooling processes.
In summary, solenoid valves play a vital role in optimizing the performance of HVAC systems. Their precise control, energy efficiency, fault detection capabilities, system protection, and compatibility with automation make them essential components in the HVAC industry. HVAC systems can achieve better temperature control, energy savings, and overall functionality by incorporating solenoid valves.
Solenoid Valves in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Ensuring Precise Fluid Control
In the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry, precise control over fluid flow is paramount to ensure the production process’s quality, safety, and efficiency. Solenoid valves play a crucial role in achieving this level of control, offering numerous benefits and applications within pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. Let’s explore how solenoid valves contribute to ensuring precise fluid control in this industry.
- Accurate Dosing: Solenoid valves provide precise control over the dosage of various liquids, allowing pharmaceutical manufacturers to maintain accurate and consistent amounts of ingredients in their formulations. This level of accuracy is vital in ensuring the potency and efficacy of medications.
- Batch Processing: Pharmaceutical manufacturing often involves batch processing, where specific quantities of ingredients need to be mixed and processed in a controlled manner. Solenoid valves enable automated and precise control over the flow of fluids during the batch processing stage, ensuring the correct ratios and timing.
- Cleanroom Compatibility: Cleanroom environments are crucial in pharmaceutical manufacturing to maintain sterility and prevent contamination. Solenoid valves are designed to meet the stringent requirements of cleanrooms, with materials and constructions compatible with the sterile conditions necessary in pharmaceutical production facilities.
- Fluid Isolation: Solenoid valves allow for efficient isolation of fluids, preventing cross-contamination and ensuring the integrity of the manufacturing process. By rapidly opening and closing, solenoid valves can create a reliable barrier between different fluids and prevent unwanted mixing.
- Process Automation: Solenoid valves can be easily integrated into automated systems, enabling seamless control and monitoring of fluid flow. This automation reduces the risk of human error, enhances process efficiency, and facilitates real-time data collection for quality control and regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, solenoid valves are indispensable in pharmaceutical manufacturing, as they enable precise fluid control, accurate dosing, and efficient batch processing. Their compatibility with cleanroom environments, fluid isolation capabilities, and seamless integration with automation systems make them essential tools for ensuring the quality, safety, and productivity of pharmaceutical production processes. Solenoid valves are vital in maintaining the high standards required in the pharmaceutical industry, enabling manufacturers to deliver safe and effective medications to patients worldwide.
Solenoid Valves in Agriculture: Applications in Irrigation and Crop Production
Irrigation is crucial in modern agriculture, ensuring optimal water distribution for crop growth and maximizing agricultural productivity. Solenoid valves have become indispensable components in irrigation systems due to their reliability, precision, and ease of automation. These valves are electromechanical devices that use an electric current to control the flow of liquids or gases through a pipe or tube. In the context of agriculture, solenoid valves find wide-ranging applications in irrigation and crop production. Here are some key points highlighting their significance:
- Efficient Water Management: Solenoid valves enable efficient water management in irrigation systems by providing precise control over water flow. They can be programmed to open and close at specific intervals, allowing for accurate irrigation scheduling and preventing overwatering or underwatering of crops.
- Automated Operation: Their electrical control mechanism allows solenoid valves to be easily integrated into automated irrigation systems. By connecting them to sensors, timers, or weather-based controllers, farmers can automate the irrigation process, ensuring that crops receive water at the right time and in the right amount.
- Drip Irrigation Systems: Solenoid valves are commonly used in drip irrigation systems, which deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing water wastage. These valves regulate water flow to individual emitters or drip lines, ensuring uniform water distribution across the field.
- Fertilizer and Chemical Injection: Solenoid valves can be employed to control the injection of fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals into the irrigation system. This enables the precise application of agrochemicals, minimizing wastage and ensuring crops receive the necessary nutrients and protection against pests and diseases.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Farmers can remotely monitor and control the irrigation process by integrating solenoid valves with advanced irrigation management systems. This allows for real-time adjustments, troubleshooting, and efficient water resource utilization.
In summary, solenoid valves are vital in modern agriculture by facilitating efficient water management, enabling automation, and enhancing crop productivity. Their use in irrigation systems ensures precise control over water flow, promotes sustainable farming practices, and contributes to agricultural operations’ overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Solenoid Valves in Packaging Industry: Enhancing Packaging Process and Accuracy
Efficiency and accuracy are paramount in the fast-paced and highly competitive packaging industry. Solenoid valves are crucial in achieving these objectives by providing precise and reliable control over fluid and gas flows. Let’s explore how solenoid valves enhance the packaging process and ensure accuracy:
- Improved Control: Solenoid valves offer fast response times and precise control over fluid and gas flows. This level of control enables packaging machines to accurately dispense and control the flow of liquids, gases, and granular materials during the packaging process. Whether filling bottles with liquids, dispensing powders, or controlling compressed air flow, solenoid valves ensure consistent and accurate performance.
- Quick and Efficient Operation: Packaging machines require a rapid and efficient operation to meet production demands. Solenoid valves, with their ability to open and close quickly, enable the packaging process to run smoothly and efficiently. They can handle high flow rates and provide instant shut-off, reducing wastage and increasing productivity.
- Versatility: Solenoid valves offer various configurations, sizes, and materials to suit various packaging applications. Whether it’s handling aggressive chemicals, food products, or sensitive pharmaceuticals, solenoid valves are designed to meet specific industry requirements. This versatility ensures compatibility with different packaging processes and materials.
- Reliability and Longevity: The packaging industry often operates in demanding environments with continuous production cycles. Solenoid valves are known for their robustness and durability, making them ideal for such conditions. Their design minimizes the risk of leaks and can withstand high pressures and temperatures, ensuring reliable performance over an extended period.
- Automation Integration: With the increasing adoption of automation in the packaging industry, solenoid valves seamlessly integrate with control systems and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). This integration allows for precise and synchronized control over multiple valves, enhancing the overall packaging process and enabling efficient management of different packaging stages.
In conclusion, solenoid valves play a vital role in the packaging industry by enhancing the packaging process and ensuring accuracy. Their ability to provide precise control, quick operation, versatility, reliability, and seamless integration with automation systems makes them indispensable components in modern packaging machines. Solenoid valves enable packaging companies to meet the demands of high-speed production, improve efficiency, reduce wastage, and maintain the quality and accuracy of packaged products.
Solenoid Valves in Chemical Processing: Safeguarding against Hazardous Substances
Chemical processing plants operate in environments where the handling and control of hazardous substances are of paramount importance. Solenoid valves ensure these plants’ safe and efficient operation by effectively managing the flow of hazardous liquids and gases. Here are some key points highlighting the significance of solenoid valves in chemical processing and their role in safeguarding against hazardous substances:
- Precise Flow Control: Solenoid valves enable precise control over the flow of hazardous substances, allowing operators to regulate the amount and rate at which chemicals are transferred within the processing system. This ensures optimal operation and minimizes the risk of leaks or spills.
- Safety Shut-off: Solenoid valves can act as safety shut-off devices in an emergency or malfunction. They can quickly and automatically shut off the flow of hazardous substances, preventing further release and potential accidents. This feature is critical in preventing catastrophic incidents like fires, explosions, or chemical leaks.
- Corrosion Resistance: Chemical processing environments often involve corrosive substances that can damage conventional valves. Solenoid valves designed for chemical processing applications are constructed using materials resistant to corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability and minimizing the risk of leaks or failures.
- Remote Operation: Many solenoid valves used in chemical processing plants can be operated remotely, allowing operators to control the flow of hazardous substances from a safe distance. This feature enhances operator safety by minimizing exposure to potentially harmful chemicals.
- Redundancy and Reliability: Solenoid valves are often incorporated into chemical processing systems with redundancy in mind. Multiple valves are installed to provide backup and ensure continuous operation. This redundancy enhances reliability and mitigates the risk of system failures or process interruptions.
Solenoid valves are a critical component in chemical processing plants, playing a vital role in safeguarding against hazardous substances. By providing precise flow control, safety shut-off capabilities, corrosion resistance, remote operation, and system redundancy, solenoid valves contribute to the overall safety, efficiency, and reliability of chemical processing operations. Their presence helps protect personnel, the environment, and valuable assets, ensuring that chemical processing facilities operate in a secure and controlled manner.

