If you’re new to the world of display interfaces, you may have come across the term DisplayPort. But what exactly is DisplayPort, and how does it differ from other interfaces like HDMI? In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of DisplayPort, its functionality, applications, different versions, connectors, and cables. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of DisplayPort and its benefits. Plus, we’ll introduce you to a product that can enhance your DisplayPort experience. Let’s dive in!
What is DisplayPort?
DisplayPort is a digital display interface that allows you to connect your computer or other devices to external displays, such as monitors or projectors. It was developed by VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) to provide a versatile and high-performance solution for transmitting audio and video signals. DisplayPort uses packet-based data transmission, which means it sends data in small packets, similar to how data is transmitted over the internet.
How Does DisplayPort Work?
DisplayPort uses a unique signaling technology called “Micro-Packet Architecture” to transmit audio and video signals. It utilizes a main link, which carries the bulk of the data, and an auxiliary channel that carries additional information like audio, control signals, and device identification.
DisplayPort also supports features like Multi-Stream Transport (MST) for daisy-chaining multiple displays and High Bit Rate 3 (HBR3) for increased bandwidth, enabling higher resolutions and refresh rates.
What is DisplayPort Used for?
DisplayPort finds applications in various industries and settings. It is widely used in computer systems, including laptops, desktops, and workstations, to connect to external monitors or projectors.
DisplayPort is especially popular among gamers and graphic designers who require high-resolution displays and smooth graphics performance. It is also utilized in professional settings like video editing studios, where color accuracy and image fidelity are paramount.
Different Versions of DisplayPort
DisplayPort has evolved over the years, with each new version introducing enhancements and additional features. It’s important to ensure that your devices support compatible versions to fully utilize these advanced features.
DisplayPort 1.0: Released in 2006, this was the first version of DisplayPort. It supports resolutions up to 2560×1600 at 60Hz.
DisplayPort 1.1: Released in 2007, this version added support for Dual-Mode DisplayPort, which allows it to be used with DVI and HDMI displays. It also added support for HDCP 1.3.
DisplayPort 1.2: Released in 2010, this version added support for higher resolutions and refresh rates. It supports resolutions up to 4096×2160 at 60Hz and 2560×1600 at 120Hz. It also added support for Display Stream Compression (DSC), which can be used to transmit higher resolutions and refresh rates over a single DisplayPort cable.
DisplayPort 1.3: Released in 2014, this version added support for HDR (High Dynamic Range) and increased the maximum bandwidth to 32.4 Gbps. It also added support for Multi-Stream Transport (MST), which allows multiple displays to be connected to a single DisplayPort output.
DisplayPort 2.0: Released in 2019, this version added support for even higher resolutions and refresh rates. It supports resolutions up to 8K at 60Hz and 16K at 30Hz. It also added support for new features such as Dynamic HDR, Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), and Variable Refresh Rate (VRR).
DisplayPort 2.1: Released in 2022, this version added support for even higher resolutions and refresh rates, as well as new features such as Dynamic HDR, Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), and Variable Refresh Rate (VRR).
DisplayPort Connectors and Cables
DisplayPort connectors come in different forms, including the standard DisplayPort, Mini DisplayPort, and USB Type-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode. These connectors vary in size and shape, and the choice depends on your device’s compatibility and available ports.
Additionally, DisplayPort cables come in different lengths and specifications. It’s essential to use certified cables that support the required version and bandwidth for optimal performance.
Is DisplayPort Better than HDMI?
One common question that arises is whether DisplayPort is better than HDMI. The answer depends on your specific needs. DisplayPort excels in terms of higher bandwidth, support for higher resolutions and refresh rates, and compatibility with advanced features like Adaptive Sync.
HDMI, on the other hand, is more commonly found in consumer electronics and home theater setups. Ultimately, the choice between DisplayPort and HDMI depends on factors such as the devices you own and the features you require.
Home Theater Setups: For home theater setups, HDMI is often the preferred choice. Many TVs lack a DisplayPort input, making HDMI more compatible with consumer electronics.
Gaming Consoles and PC Gaming: HDMI 2.0 or higher is typically the only output available on gaming consoles, making it the primary choice. However, for PC gaming, DisplayPort is generally the better option if your computer supports it, offering higher refresh rates and compatibility with advanced gaming features.
Laptop to TV/Projector Connections: When connecting a laptop to a TV or projector, HDMI is a safe bet as it is widely supported by most devices.
Multiple Monitor Setups: If you need to connect your laptop to multiple monitors, DisplayPort is the preferred choice. HDMI typically supports a single screen, while DisplayPort allows for daisy-chaining or using multi-stream transport (MST) to connect multiple monitors.
Adapter Usage: If you need to connect a device with only an HDMI output to a DisplayPort input (or vice versa), you can use an adapter to bridge the connection.
Consider these factors to make an informed decision based on your specific needs and device compatibility. Whether you choose DisplayPort or HDMI, both offer their own unique advantages. Selecting the right cable will ensure optimal performance and enhance your overall display experience.
Summary
In summary, DisplayPort is a versatile and high-performance display interface that offers numerous advantages for connecting devices to external displays. By understanding the different versions, connectors, and cables, you can optimize your DisplayPort experience and unlock the full potential of your display setup.
To further enhance your DisplayPort setup, we recommend the AV Access 4KSW21-DK KVM Switch with Docking Station. This innovative product combines a KVM switch and a docking station, providing seamless switching between multiple computers and convenient connectivity for peripherals.
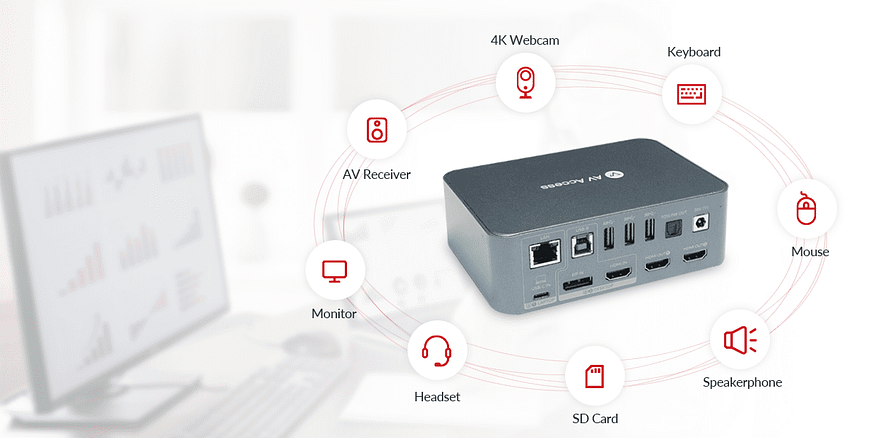
It not only supports DisplayPort but also offers compatibility with HDMI. This flexibility ensures high-quality video transmission and enables you to maximize the capabilities of your devices.
Whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or professional in need of precise visuals, DisplayPort provides stunning resolutions, smooth graphics, and enhanced productivity. By selecting the right version, connectors, and cables, you can fully leverage the benefits of this exceptional display interface.
Embrace the power of DisplayPort and elevate your display experience to new heights. Explore the possibilities, make the right connections, and enjoy the incredible features that DisplayPort and the AV Access 4KSW21-DK KVM Switch with Docking Station have to offer.
You May Also be Interested
Gamers’ thoughts: Shall I Use DisplayPort or HDMI?
HDMI 2.0 vs 2.1: Facts to Know Before Paying Your Money
HDMI Splitters: An Ultimate Guide for Beginners 2023
KVM Switch vs. Docking Station: Which Shall I Choose?
About AV Access
AV Access is an experienced manufacturer that produces quality HDMI extenders, KVM extenders, wireless presentation systems, etc. and we also offer AV over IP solutions for scalable uses. These products — HDBaseT extender, and 4K HDMI extender — are among our best-sellers.
Are you a newbie? AV Access blog helps beginners to get on board easily (visit and learn about KVM extenders, USB extenders, and more).
Original Copy: https://www.avaccess.com/blogs/guides/what-is-displayport/

